我们知道微博可以在编辑中添加话题,比如将两个"#"号之间的字体变为蓝色等,最近项目当中需要用到这样的功能,就考虑了一下如何实现这个功能~
首先说一下我们的要求:
- 两个 “#” 号之间的字体变为蓝色
- 两个 “#” 为一对,第二对 “#” 号则是从第3个 “#” 到第四个 “#” 之间的字符
- “#” 号中的字符为空或则多过20个为无效话题,不变蓝色
思路:
- 要想要显示不一样颜色的字体在
UITextView 中,我们不用 CoreText 也不用 UITextKit,就用最简单的 NSMutableAttributedString,使用 NSMutableAttributedString 可以将特殊范围内的字符标记为不同的样式.
- 使用正则来搜索符合标准的字符串所处的位置,用来改变此段字符的格式
- 监听
UITextView 的字符改变,每改变一次就将所有的字符重新匹配一遍,绘制富文本,并赋值给 UITextView
使用NSMutableAttributedString标记特殊字符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
UITextView *textView = [[UITextView alloc]init];
textView.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
textView.backgroundColor = [UIColor lightGrayColor];
textView.frame = CGRectMake(0, 0, 300, 300);
textView.center = self.view.center;
textView.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:30];
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedStr = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc]initWithString:@"给#时间#一点时间!"];
[attributedStr addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName value:[UIColor blueColor] range:NSMakeRange(1, 4)];
[attributedStr addAttribute:NSFontAttributeName value:[UIFont systemFontOfSize:25] range:NSMakeRange(0, 10)];
textView.attributedText = attributedStr;
[self.view addSubview:textView];
}
|

通过正则来搜索符合标准的字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| // 传入一个字符串,返回排版好的attributedString
+ (NSMutableAttributedString *)attriStrUseTagModelWithStr:(NSString *)dataStr
{
// 创建一个attriStr
NSMutableAttributedString *attriStr = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc]initWithString:dataStr];
BOOL endSearch = NO;
// 循环收索符合标准的字符串
do {
// 通过正则来搜索字符串
NSRange range = [dataStr rangeOfString:@"#[^#]{1,20}?#" options:NSRegularExpressionSearch range:NSMakeRange(0, dataStr.length)];
// 如果收索完就退出循环
if (range.location == NSNotFound) {
endSearch = YES;
}
else{
// 将符合标准的区间标记为蓝色
[attriStr addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName value:[UIColor blueColor] range:range];
NSMutableString *replaceStr = [NSMutableString string];
// 因为我们用的是sear收索,所以只能匹配到第一符合正则的字符串,我们需要用等长度的字符串替换调,用来收索下一个符合的字符串
for (int i = 0; i < range.length; i++) {
[replaceStr appendString:@"@"];
}
dataStr = [dataStr stringByReplacingCharactersInRange:range withString:replaceStr];
}
} while (!endSearch);
return attriStr;
}
|
结合我们以上内容我们自定义一个UITextView,当你输入的时候就实时替换富文本
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| #import "BZFilterTextView.h"
#import "BZTagSearTool.h"
@interface BZFilterTextView ()
@end
@implementation BZFilterTextView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(CGRect)frame
{
self = [super initWithFrame:frame];
if (self) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(textdidChange:) name:UITextViewTextDidChangeNotification object:self];
}
return self;
}
- (void)textdidChange:(NSNotification *)noti
{
NSRange selRange = self.selectedRange;
self.attributedText = [BZTagSearTool attriStrUseTagModelWithStr:self.text];
self.selectedRange = selRange;
}
- (void)dealloc
{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self];
}
@end
|
结合以上的内容我们来自定义一个textView,可以在输入的时候实时替换textView
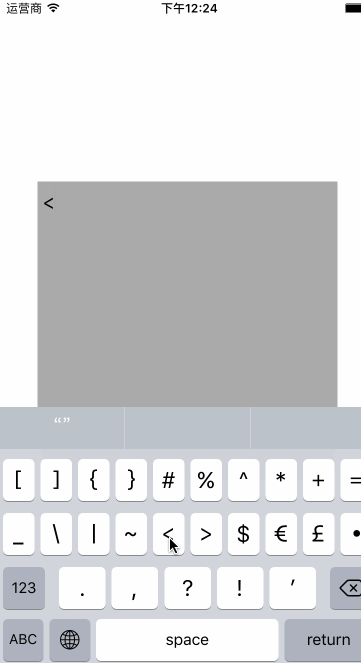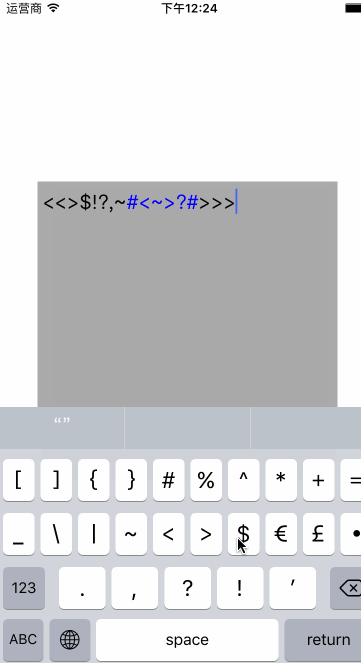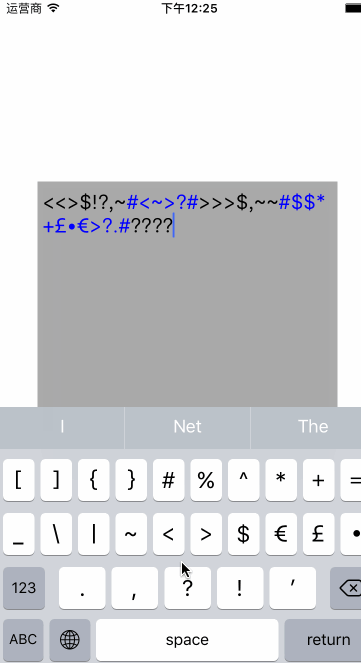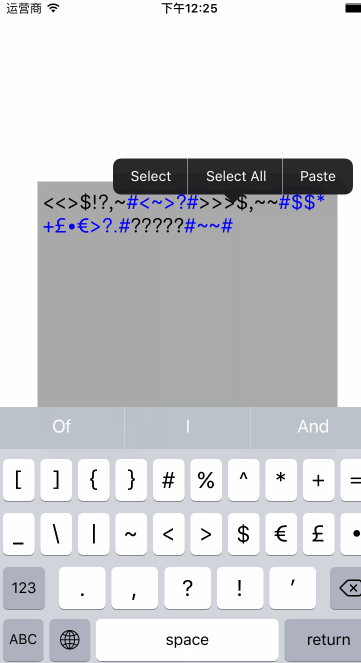
注意的问题:
- 因为正则收索用的是sear所以要将已经收到的内容用其他的非#符号代替
- 在设置textView的attrituteText时,一定要将之前插入的光标位置先记录下来,在赋值后再赋值上去,以防止用户插入字符后,出现光标到末尾的现象
接下来要说一个严重的bug,这是我在输入中文字符中发现的,大概是这个样子的:
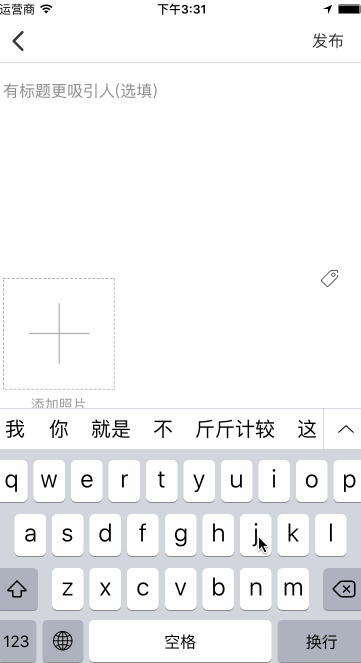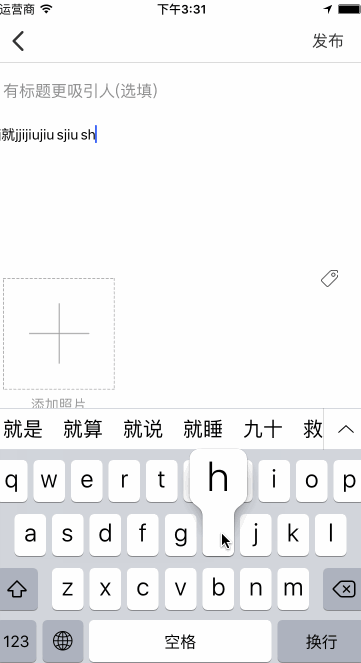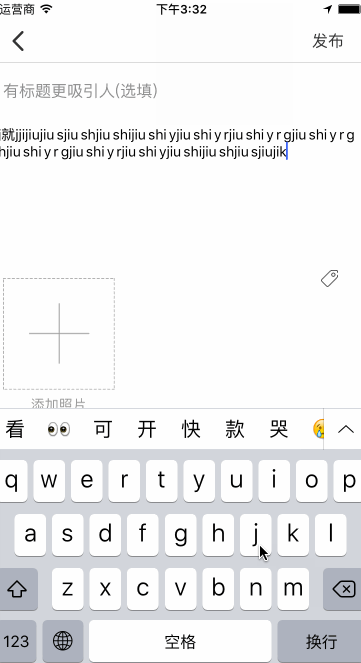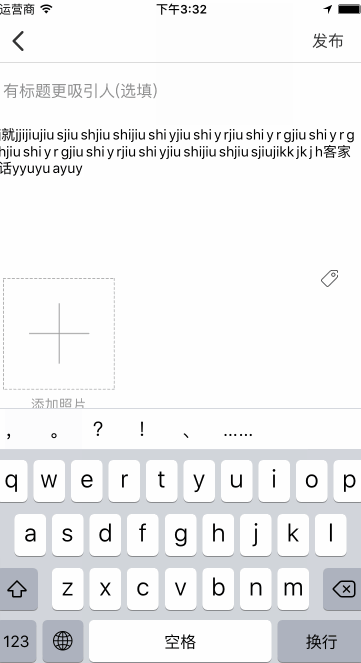
这也是实现这个东西困扰我最大的问题,我当时无论如何都想不通,为什么会记录上一次输入的字符并和这次输入的加一块返回回来,还在中间加了一个空格,说下当时我想过的几个思路:
-
首先,我想到的是因为通过键盘输入的是记录在 text 中的,而我重新赋值是通过 attributeText 赋值的,这两个属性都能够改变 textView 所显示的内容,可能是因为赋值的冲突导致的,那我把 text 在赋值前给清空,结果发现,清空后还是会记录原来的值
-
为了测试到底能不能清空,我干脆把 attributeText 也给清空了,最后发现还是会记录原来的值,那这种方法不行,那为什么无法删除储存的值呢
-
不知道大家注意到没有,我们使用英文输入法的时候并没有这个问题,难道是因为输入法的问题,可是输入法怎么会影响 text 的值的储存呢,或许是应为汉字的字符长度和字母不同,导致我计算的 range 有误,但是打印证明我的计算没有出现错误…(::>_<:😃
-
后来的后来,我甚至想到了每次输入就重新创建一个 textView,发现我是用汉字输入法在未确认联想提供的汉字或者回车使用字母是取出的值是空,这也提醒了我,我之所以取不到值,是因为,虽然字母已经显示在了textVeiw 上,但是它处于一种联想输入汉字的高亮状态,而不是真实的输入值
-
我前面把值设置为空,是把真实的值设置为空,但是联想输入的字符在一个我不知道的地方储存着,解决的办法就是,监听当前是否处于联想输入的状态,这个时候不对字符串做处理,当真的显示在 textView 上的值时,在做处理,实现的方式很简单,在 textView 的值改变方法里监听状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| - (void)textdidChange:(NSNotification *)noti
{
UITextRange *selectedRange = [self markedTextRange];
UITextPosition *position = [self positionFromPosition:selectedRange.start offset:0];
if (!position) {
NSRange selRange = self.selectedRange;
NSMutableAttributedString *str = [BZTagStringTool attriStrUseTagModelWithStr:self.text];
self.attributedText = str;
self.selectedRange = selRange;
}
}
|
当处于联想输入的时候,虽然监听到 textView 发生值改变,但是其实并未将其作为 textView 的内容储存起来~~切记!!!
下面是字符搜索的 swift 版本,可以在 oc 中使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class BZTagStringTool: NSObject {
class func attriStrUseTagModelWithStr(str:String) -> NSMutableAttributedString {
let attriStr = NSMutableAttributedString(string: str)
var dataStr = str
var endSearch = false
while !endSearch {
let range = (dataStr as NSString).rangeOfString("#[^#]{1,20}?#", options: .RegularExpressionSearch)
if range.location != NSNotFound {
attriStr.addAttribute(NSForegroundColorAttributeName, value: UIColorFromRGB(0x5298e6), range: range)
let replaceStr = NSMutableString()
for _ in 0..<range.length {
replaceStr.appendString("@")
}
dataStr = (dataStr as NSString).stringByReplacingCharactersInRange(range, withString: replaceStr as String)
}
else
{
endSearch = true
}
}
attriStr.addAttributes([NSFontAttributeName:UIFont.systemFontOfSize(14)], range: NSMakeRange(0, str.characters.count))
return attriStr
}
}
|



